Localization
ABP's localization system is seamlessly integrated to the Microsoft.Extensions.Localization package and compatible with the Microsoft's localization documentation. It adds some useful features and enhancements to make it easier to use in real life application scenarios.
Volo.Abp.Localization Package
This package is already installed by default with the startup template. So, most of the time, you don't need to install it manually.
Volo.Abp.Localization is the core package of the localization system. Install it to your project using the package manager console (PMC):
Install-Package Volo.Abp.Localization
Then you can add AbpLocalizationModule dependency to your module:
using Volo.Abp.Modularity;
using Volo.Abp.Localization;
namespace MyCompany.MyProject
{
[DependsOn(typeof(AbpLocalizationModule))]
public class MyModule : AbpModule
{
//...
}
}
Creating A Localization Resource
A localization resource is used to group related localization strings together and separate them from other localization strings of the application. A module generally defines its own localization resource. Localization resource is just a plain class. Example:
public class TestResource
{
}
Then it should be added using AbpLocalizationOptions as shown below:
[DependsOn(typeof(AbpLocalizationModule))]
public class MyModule : AbpModule
{
public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
Configure<AbpVirtualFileSystemOptions>(options =>
{
// "YourRootNameSpace" is the root namespace of your project. It can be empty if your root namespace is empty.
options.FileSets.AddEmbedded<MyModule>("YourRootNameSpace");
});
Configure<AbpLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
//Define a new localization resource (TestResource)
options.Resources
.Add<TestResource>("en")
.AddVirtualJson("/Localization/Resources/Test");
});
}
}
In this example;
- Added a new localization resource with "en" (English) as the default culture.
- Used JSON files to store the localization strings.
- JSON files are embedded into the assembly using
AbpVirtualFileSystemOptions(see virtual file system).
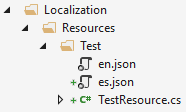
JSON files are located under "/Localization/Resources/Test" project folder as shown below:
A JSON localization file content is shown below:
{
"culture": "en",
"texts": {
"HelloWorld": "Hello World!"
}
}
- Every localization file should define the
culturecode for the file (like "en" or "en-US"). textssection just contains key-value collection of the localization strings (keys may have spaces too).
Default Resource
AbpLocalizationOptions.DefaultResourceType can be set to a resource type, so it is used when the localization resource was not specified:
Configure<AbpLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
options.DefaultResourceType = typeof(TestResource);
});
The application startup template sets
DefaultResourceTypeto the localization resource of the application.
See the Client Side section below for a use case.
Short Localization Resource Name
Localization resources are also available in the client (JavaScript) side. So, setting a short name for the localization resource makes it easy to use localization texts. Example:
[LocalizationResourceName("Test")]
public class TestResource
{
}
See the Getting Localized Test / Client Side section below.
Inherit From Other Resources
A resource can inherit from other resources which makes possible to re-use existing localization strings without referring the existing resource. Example:
[InheritResource(typeof(AbpValidationResource))]
public class TestResource
{
}
Alternative inheritance by configuring the AbpLocalizationOptions:
services.Configure<AbpLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
options.Resources
.Add<TestResource>("en") //Define the resource by "en" default culture
.AddVirtualJson("/Localization/Resources/Test") //Add strings from virtual json files
.AddBaseTypes(typeof(AbpValidationResource)); //Inherit from an existing resource
});
- A resource may inherit from multiple resources.
- If the new resource defines the same localized string, it overrides the string.
Extending Existing Resource
Inheriting from a resource creates a new resource without modifying the existing one. In some cases, you may want to not create a new resource but directly extend an existing resource. Example:
services.Configure<AbpLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
options.Resources
.Get<TestResource>()
.AddVirtualJson("/Localization/Resources/Test/Extensions");
});
- If an extension file defines the same localized string, it overrides the string.
Getting Localized Texts
Server Side
Getting the localized text on the server side is pretty standard.
Simplest Usage In A Class
public class MyService
{
private readonly IStringLocalizer<TestResource> _localizer;
public MyService(IStringLocalizer<TestResource> localizer)
{
_localizer = localizer;
}
public void Foo()
{
var str = _localizer["HelloWorld"];
}
}
Format Arguments
Format arguments can be passed after the localization key. If your message is Hello {0}, welcome!, then you can pass the {0} argument to the localizer like _localizer["HelloMessage", "John"]
Simplest Usage In A Razor View/Page
@inject IHtmlLocalizer<TestResource> Localizer
<h1>@Localizer["HelloWorld"]</h1>
Refer to the Microsoft's localization documentation for details about using localization on the server side.
Client Side
ABP provides JavaScript services to use the same localized texts in the client side.
getResource
abp.localization.getResource function is used to get a localization resource:
var testResource = abp.localization.getResource('Test');
Then you can localize a string based on this resource:
var str = testResource('HelloWorld');
localize
abp.localization.localize function is a shortcut where you can both specify the text name and the resource name:
var str = abp.localization.localize('HelloWorld', 'Test');
HelloWorld is the text to localize, where Test is the localization resource name here.
If you don't specify the localization resource name, it uses the default localization resource defined on the AbpLocalizationOptions (see the Default Resource section above). Example:
var str = abp.localization.localize('HelloWorld'); //uses the default resource
Format Arguments
If your localized string contains arguments, like Hello {0}, welcome!, you can pass arguments to the localization methods. Examples:
var str1 = abp.localization.getResource('Test')('HelloWelcomeMessage', 'John');
var str2 = abp.localization.localize('HelloWorld', 'Test', 'John');
Both of the samples above produce the output Hello John, welcome!.