How to Make HTTP Requests
About HttpClient
Angular has the amazing HttpClient for communication with backend services. It is a layer on top and a simplified representation of XMLHttpRequest Web API. It also is the recommended agent by Angular for any HTTP request. There is nothing wrong with using the HttpClient in your ABP project.
However, HttpClient leaves error handling to the caller (method). In other words, HTTP errors are handled manually and by hooking into the observer of the Observable returned.
getConfig() {
this.http.get(this.configUrl).subscribe(
config => this.updateConfig(config),
error => {
// Handle error here
},
);
}
Although clear and flexible, handling errors this way is repetitive work, even when error processing is delegated to the store or any other injectable.
An HttpInterceptor is able to catch HttpErrorResponse and can be used for a centralized error handling. Nevertheless, cases where default error handler, therefore the interceptor, must be disabled require additional work and comprehension of Angular internals. Check this issue for details.
RestService
ABP core module has a utility service for HTTP requests: RestService. Unless explicitly configured otherwise, it catches HTTP errors and dispatches a RestOccurError action. This action is then captured by the ErrorHandler introduced by the ThemeSharedModule. Since you should already import this module in your app, when the RestService is used, all HTTP errors get automatically handled by default.
Getting Started with RestService
In order to use the RestService, you must inject it in your class as a dependency.
import { RestService } from '@abp/ng.core';
@Injectable({
/* class metadata here */
})
class DemoService {
constructor(private rest: RestService) {}
}
You do not have to provide the RestService at module or component/directive level, because it is already provided in root.
How to Make a Request with RestService
You can use the request method of the RestService is for HTTP requests. Here is an example:
getFoo(id: number) {
const request: Rest.Request<null> = {
method: 'GET',
url: '/api/some/path/to/foo/' + id,
};
return this.rest.request<null, FooResponse>(request);
}
The request method always returns an Observable<T>. Therefore you can do the following wherever you use getFoo method:
doSomethingWithFoo(id: number) {
this.demoService.getFoo(id).subscribe(
foo => {
// Do something with foo.
}
)
}
You do not have to worry about unsubscription. The RestService uses HttpClient behind the scenes, so every observable it returns is a finite observable, i.e. it closes subscriptions automatically upon success or error.
As you see, request method gets a request options object with Rest.Request<T> type. This generic type expects the interface of the request body. You may pass null when there is no body, like in a GET or a DELETE request. Here is an example where there is one:
postFoo(body: Foo) {
const request: Rest.Request<Foo> = {
method: 'POST',
url: '/api/some/path/to/foo',
body
};
return this.rest.request<Foo, FooResponse>(request);
}
You may check here for complete Rest.Request<T> type, which has only a few changes compared to HttpRequest class in Angular.
How to Disable Default Error Handler of RestService
The request method, used with defaults, always handles errors. Let's see how you can change that behavior and handle errors yourself:
deleteFoo(id: number) {
const request: Rest.Request<null> = {
method: 'DELETE',
url: '/api/some/path/to/foo/' + id,
};
return this.rest.request<null, void>(request, { skipHandleError: true });
}
skipHandleError config option, when set to true, disables the error handler and the returned observable starts throwing an error that you can catch in your subscription.
removeFooFromList(id: number) {
this.demoService.deleteFoo(id).subscribe(
foo => {
// Do something with foo.
},
error => {
// Do something with error.
}
)
}
How to Get a Specific API Endpoint From Application Config
Another nice config option that request method receives is apiName (available as of v2.4), which can be used to get a specific module endpoint from application configuration.
putFoo(body: Foo, id: string) {
const request: Rest.Request<Foo> = {
method: 'PUT',
url: '/' + id,
body
};
return this.rest.request<Foo, void>(request, {apiName: 'foo'});
}
putFoo above will request https://localhost:44305/api/some/path/to/foo/{id} as long as the environment variables are as follows:
// environment.ts
export const environment = {
apis: {
default: {
url: 'https://localhost:44305',
},
foo: {
url: 'https://localhost:44305/api/some/path/to/foo',
},
},
/* rest of the environment variables here */
}
How to Observe Response Object or HTTP Events Instead of Body
RestService assumes you are generally interested in the body of a response and, by default, sets observe property as 'body'. However, there may be times you are rather interested in something else, such as a custom proprietary header. For that, the request method receives observe property in its config object.
getSomeCustomHeaderValue() {
const request: Rest.Request<null> = {
method: 'GET',
url: '/api/some/path/that/sends/some-custom-header',
};
return this.rest.request<null, HttpResponse<any>>(
request,
{observe: Rest.Observe.Response},
).pipe(
map(response => response.headers.get('Some-Custom-Header'))
);
}
You may find Rest.Observe enum here.
HTTP Error Handling
When the RestService is used, all HTTP errors are reported to the HttpErrorReporterService, and then ErrorHandler, a service exposed by the @abp/ng.theme.shared package automatically handles the errors.
Custom HTTP Error Handler
A custom HTTP error handler can be registered to an injection token named HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER. If a custom handler function is registered, the ErrorHandler executes that function.
See an example:
// http-error-handler.ts
import { ContentProjectionService, PROJECTION_STRATEGY } from '@abp/ng.core';
import { ToasterService } from '@abp/ng.theme.shared';
import { HttpErrorResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { throwError } from 'rxjs';
import { Error404Component } from './error404/error404.component';
export function handleHttpErrors(injector: Injector, httpError: HttpErrorResponse) {
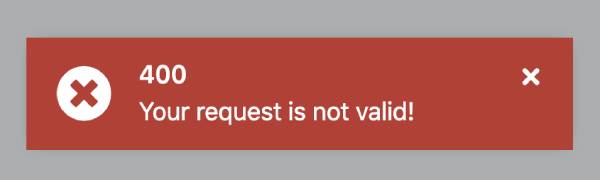
if (httpError.status === 400) {
const toaster = injector.get(ToasterService);
toaster.error(httpError.error?.error?.message || 'Bad request!', '400');
return;
}
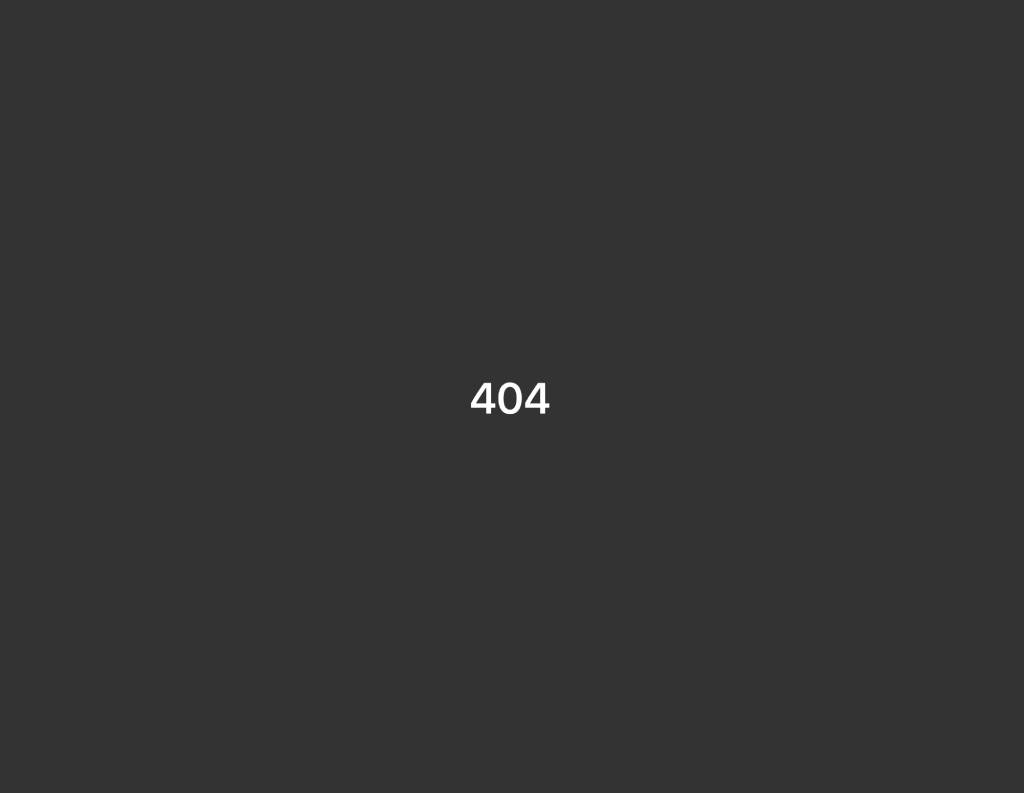
if (httpError.status === 404) {
const contentProjection = injector.get(ContentProjectionService);
contentProjection.projectContent(PROJECTION_STRATEGY.AppendComponentToBody(Error404Component));
return;
}
return throwError(httpError);
}
// app.module.ts
import { Error404Component } from './error404/error404.component';
import { handleHttpErrors } from './http-error-handling';
import { HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER, ... } from '@abp/ng.theme.shared';
@NgModule({
// ...
providers: [
// ...
{ provide: HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER, useValue: handleHttpErrors }
],
declarations: [
//...
Error404Component],
})
export class AppModule {}
In the example above:
- Created a function named
handleHttpErrorsand defined as value of theHTTP_ERROR_HANDLERprovider in app.module. After this, the function executes when an HTTP error occurs. - 400 bad request errors is handled. When a 400 error occurs, backend error message will be displayed as shown below:
- 404 not found errors is handled. When a 404 error occurs,
Error404Componentwill be appended to the<body>as shown below:
- Since
throwError(httpError)is returned at bottom of thehandleHttpErrors, theErrorHandlerwill handle the HTTP errors except 400 and 404 errors.
Note 1: If you put return to next line of handling an error, default error handling will not work for that error.
export function handleHttpErrors(injector: Injector, httpError: HttpErrorResponse) {
if (httpError.status === 403) {
// handle 403 errors here
return; // put return to skip default error handling
}
}
Note 2: If you put return throwError(httpError), default error handling will work.
throwErroris a function. It can be imported fromrxjs.httpErroris the second parameter of the error handler function which is registered to theHTTP_ERROR_HANDLERprovider. Type of thehttpErrorisHttpErrorResponse.
import { throwError } from 'rxjs';
export function handleHttpErrors(injector: Injector, httpError: HttpErrorResponse) {
if (httpError.status === 500) {
// handle 500 errors here
return;
}
// you can return the throwError(httpError) at bottom of the function to run the default handler of ABP for HTTP errors that you didn't handle above.
return throwError(httpError)
}