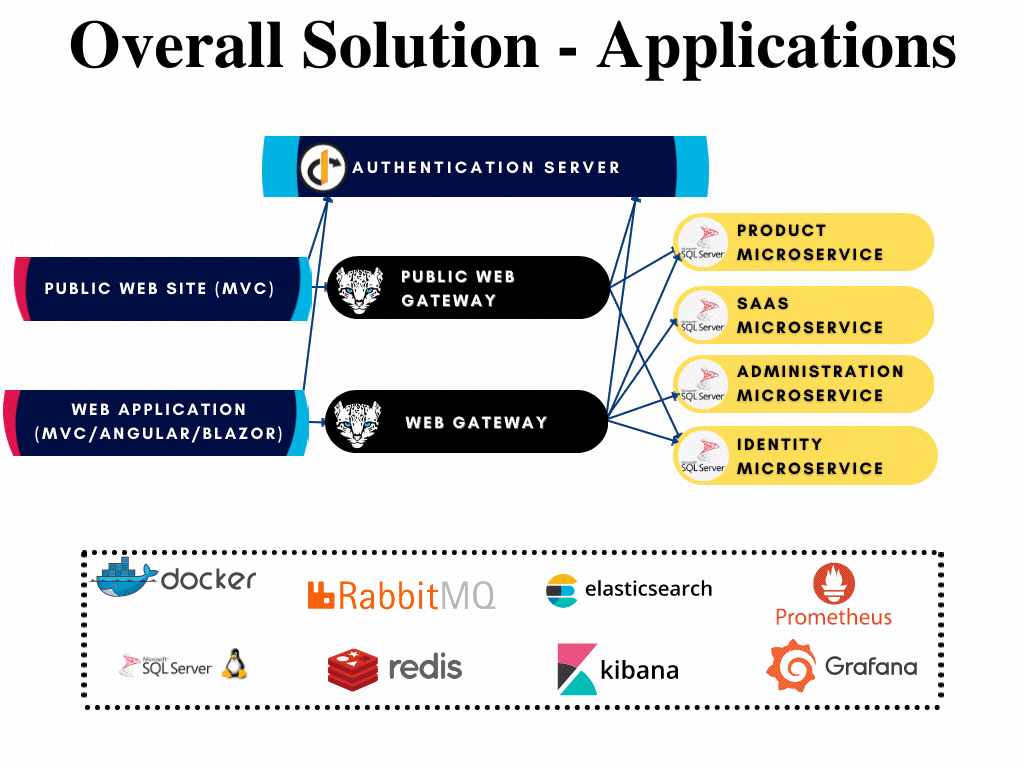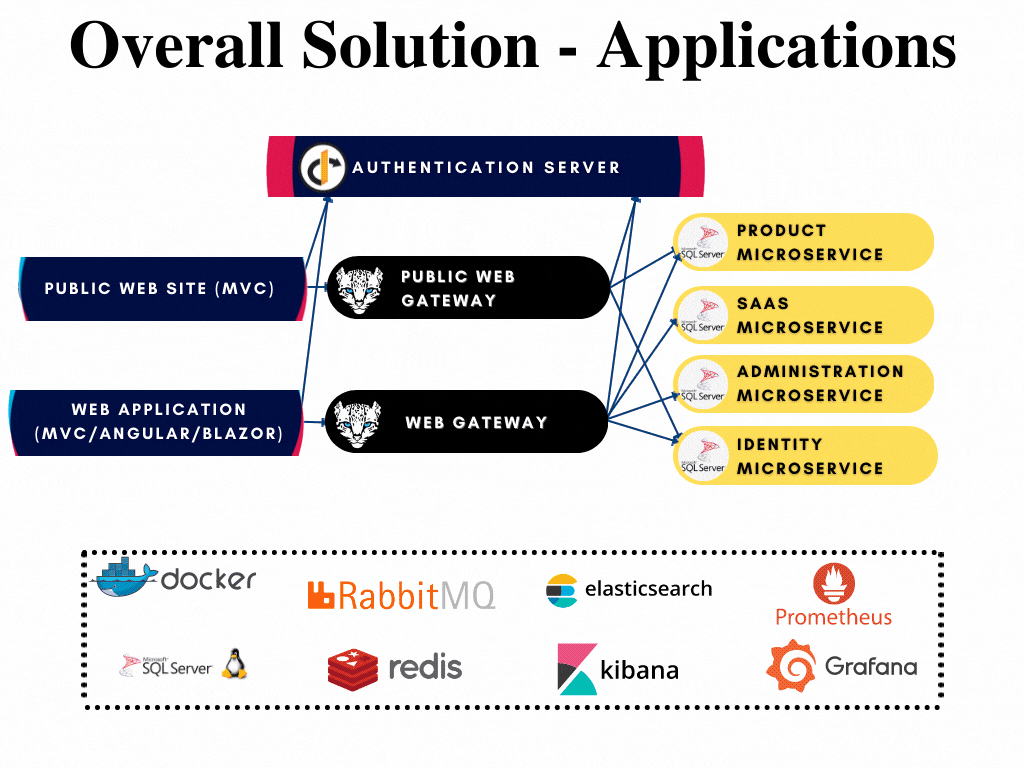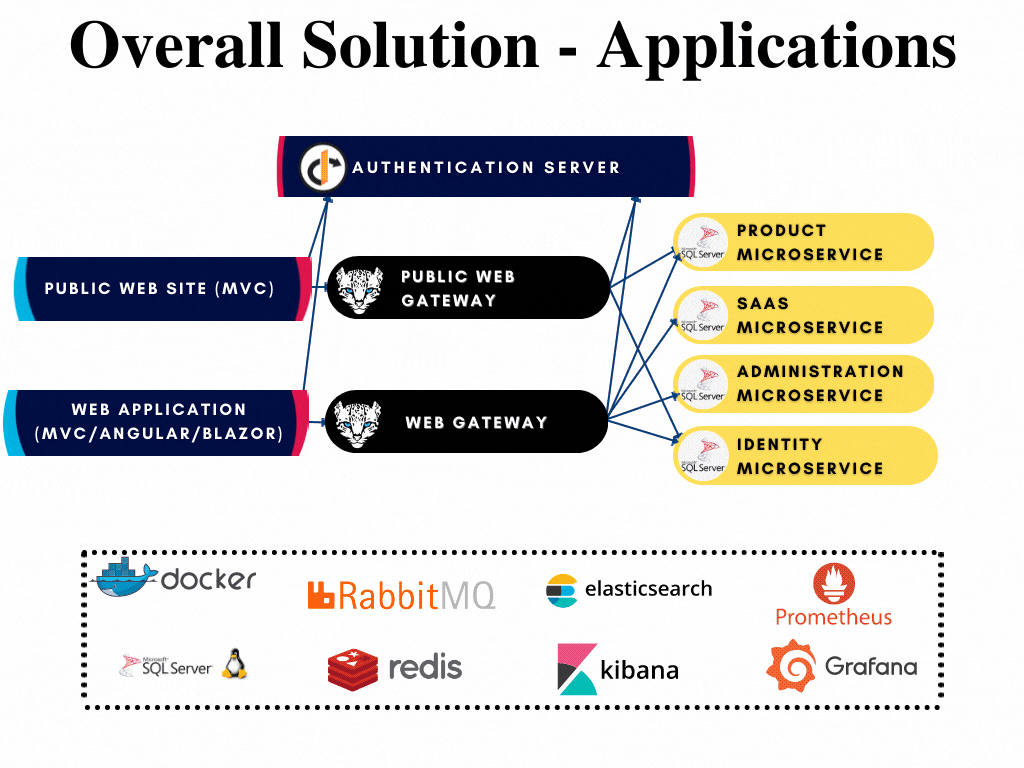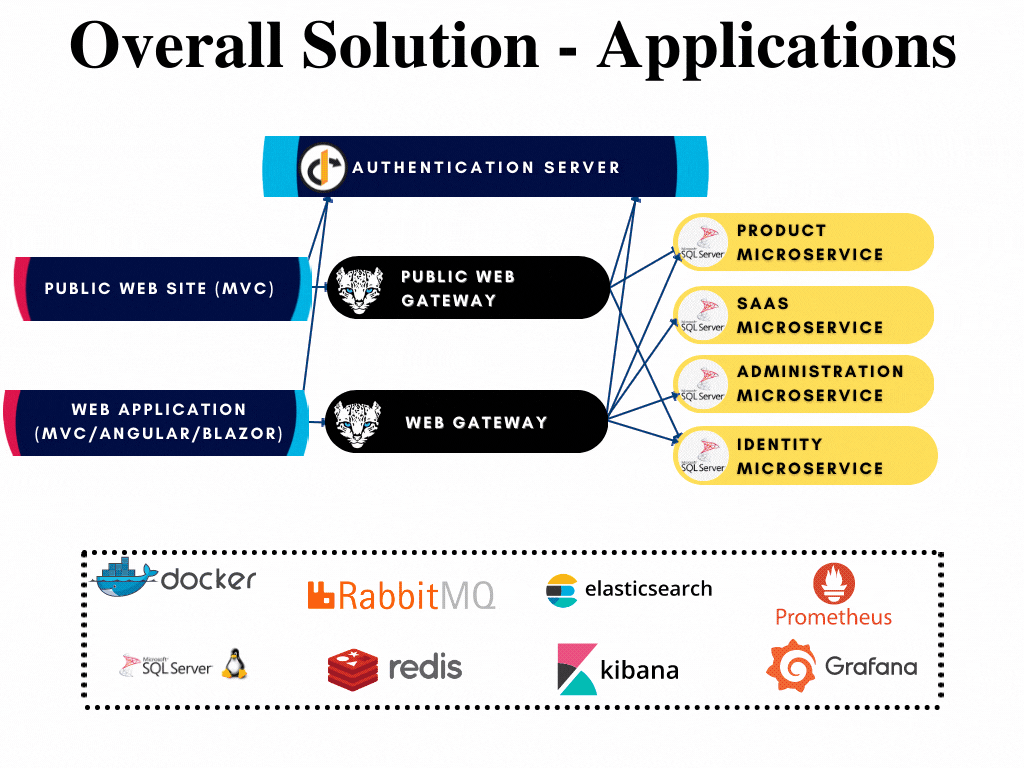
Microservice Startup Template: Applications
There are 3 different applications are presented in the microservice startup template;
- Authentication Server is located under apps/auth-server folder. This application is the single sign on and single sign out point of your application that also authenticates and authorizes your applications, gateways and microservices.
- Web (Back-office) application has Razor/MVC, Angular, Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server options. This is the main application of your solution and located under the apps/web folder.
- Public Web (Landing page) application is located under apps/public-web folder. This is the front page application of your solution.
All applications has their respected solutions created already and can be developed further when if required without opening the whole solution. The solutions are highlighted in the overall diagram shown below:
Authentication Server
The Authentication Server (named as AuthServer) is a web application that is used as the single sign-on authentication server. It hosts the public account pages such as login, register, forgot password, two factor authentication, profile management... pages, OAuth endpoints and authentication related APIs. All applications and services use this application as a central authority for the authentication. It is built upon OpenId certified IdentityServer 4.
AuthServer is the single sign-on and single sign-out server of the microservice template that handles authentication and authorization between applications. Consecutively, it is the most independent application that doesn't require any gateway or microservice to run. It only requires related databases up and running.
AuthServer references to Account Module that Account.Pro.Public.Web package serves the pages like login, sign-out, external login providers etc. and Account.Pro.Public.Application package hosts the implementations.
Account Module functionality is split between microservices;
- Identity and IdentityServer related data is kept in IdentityService microservice
- Account management and profile management related data is kept in AdministrationService microservice
- Tenant login related data is kept in SaasService microservice
AuthServer makes directly database requests to these microservices to reach related data for operating successfully. Hence depends on IdentityService EntityFrameworkCore, AdministrationService EntityFrameworkCore and SaasService EntityFrameworkCore modules and also has the configuration of related connection strings in the appsettings.json file.
Authentication & Authorization
IdentityServer4 is an implementation of OpenId Connect and Oauth2.0 protocols that uses middleware for necessary protocol headers. Based on applications; different flows are used to authenticate the clients for the resources.

Single Sign-On
When logging in to an application, user will be automatically redirected to AuthServer. If the user has already been logged in to one of the applications and try to login to other application, signing in will be immediately granted without prompting the login page.
Since login functionality is centralized, external logins like Azure, Google, Twitter, Facebook etc must be implemented in AuthServerModule as well.
Single Sign-Out
All the applications are configured to use Front-Channel Logout and Account Module already implements the necessary functionality. Whenever you logout from one of your application, you are automatically logged out of other signed in applications once you re-visit them.
If you are logged in to both Web and Public applications, if you log out from Web application; you will receive a Signed Out page noticing you that you have been signed out and redirected back. If you refresh the Public application, you will see that you are logged off from this application too.
If you want to change this behavior, update the related client data FrontChannelLogoutSessionRequired = false in the IdentityServer Management pages.
Data Seed
AuthServer needs initial identity server and admin user data to operate. See IdentityService Data Seeding.
It is a good practice to keep your IdentityServerDataSeeder up to date whenever you expand your microservice solution with new api resources and clients.
Api Resources
Api Resources are typically http api endpoints that clients wants to access. All the microservices are added as Api Resources
private async Task CreateApiResourcesAsync()
{
...
await CreateApiResourceAsync("AccountService", commonApiUserClaims);
await CreateApiResourceAsync("IdentityService", commonApiUserClaims);
await CreateApiResourceAsync("AdministrationService", commonApiUserClaims);
await CreateApiResourceAsync("SaasService", commonApiUserClaims);
await CreateApiResourceAsync("ProductService", commonApiUserClaims);
}
These are the name of the resources.
Api Scopes
Api Scopes can be considered as one-to-many parts of a resource that represents what a client application is allowed to do. They are mostly defined as myApi.read, myApi.write etc.. for authorization purposes. Abp uses Permission Management and delegates to authorization to permission management. Hence declaring one scope for each api resource
private async Task CreateApiScopesAsync()
{
await CreateApiScopeAsync("AccountService");
await CreateApiScopeAsync("IdentityService");
await CreateApiScopeAsync("AdministrationService");
await CreateApiScopeAsync("SaasService");
await CreateApiScopeAsync("ProductService");
}
Clients
Clients are the applications that want to reach api resources via allowed interactions (grant types) with the token server by representing a list (scopes) of what they request to do.
There are different clients seeded for AuthServer application;
Swagger Clients: There is a single swagger client named
WebGateway_Swaggerthat usesauthorization_codegrant type. This swagger client is allowed for all the scopes as default and used in both gateways and all microservices for swagger authorization.Back-Office Clients:
- Web Client is the Razor/MVC application client using
hybridgrant type. This client has all the scope allowance as default. - Angular is the spa application client using
authorization_codegrant type. This client has all the scope allowance as default. - Blazor Client is the Blazor WebAssembly application client using
authorization_codegrant type. This client has all the scope allowance as default. - Blazor Server is the application client using
hybridgrant type. This client has all the scope allowance as default.
- Web Client is the Razor/MVC application client using
Public/Landing Page Client: Public Web application is a Razor/MVC application client using
hybridgrant type. This client hasAccountService,AdministrationServiceandProductServicescope allowance as default.Service Clients: These are the server-to-server interactions between services. This is a
client_credentialsgrant type and there is no user or user information involved in this flow.As default, AdministrationService is declared as a client. AdministrationService requires list of user data from IdentityService. Since this endpoint is authorized with a permission, required permission is also granted on the client creation. Granted permission will be seen with ProviderName
Cunder AbpPermissionGrants table in Administration database. That indicates this is aclient_credentialgiven permission.//Administration Service Client await CreateClientAsync( name: "MyProjectName_AdministrationService", scopes: commonScopes.Union(new[] { "IdentityService" // Allowed scope to make request }), grantTypes: new[] {"client_credentials"}, secret: "1q2w3e*".Sha256(), permissions: new[] {IdentityPermissions.Users.Default} );
Deployment
Check IdentityServer deployment guide.
Web Application (Back-office)
This is the back-office (admin-side) application of the template. This application shows the module UI but does not host the module. Modules are hosted by related microservices and the back-office application just uses them as remote services. For more information, do check Module Architecture Best Practices & Conventions Section C.
To achieve this functionality, back-office application needs to reference to IdentityService, AdministrationService, SaasService and sample ProductService microservices .Web and HttpApi.Client layers to use them as remote services while microservices need to host the modules.
Therefore;
- IdentityService microservice hosts IdentityServer Management and Identity Management modules.
Identity.HttpApi.Clientproject is referenced for remote service calls but since IdentityService microservice doesn't have a Web layer; module's.Webpackages are referenced explicitly. - AdministrationService microservice hosts Text-Template Management, Language Management, Audit Logging, Lepton Theme Management modules.
Administration.HttpApi.Clientis referenced for remote service calls but since AdministrationService microservice doesn't have a Web layer; module's.Webpackages are referenced explicitly. - SaasService microservice hosts Saas Tenant and Host Management module.
Saas.HttpApi.Clientis referenced for remote service calls but since SaasService microservice doesn't have a Web layer; module's.Webpackages are referenced explicitly. - ProductService microservice doesn't host any external module and has its own Web layer with modularly developed UI. Hence forth,
ProductService.WebandProductService.HttpApi.Clientare referenced together.
Remote Service Calls - Web Gateway
The back-office application's interactions with the microservices will be through the Web Gateway. There is a related configuration for remote services in the appsettings.json:
"RemoteServices": {
"Default": {
"BaseUrl": "https://localhost:44325/"
}
},
This configuration indicates the default base url of all the Http Api requests; which is the url of the Web Gateway for the back-office application.
Application Templates
There are 4 different back-office application templates supported:
Razor/MVC
This is a server side application that you can use both Razor Pages and MVC Controllers. As a recommended flow for server side clients, this application uses hybrid flow. This client is being seeded in IdentityServerDataSeeder with MyProjectName_Web client name with all the available scopes.
In the WebModule authorization is configured as below to be able to make request to all the api resources and some basic identity resources:
context.Services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
...
})
.AddCookie("Cookies", options =>
{
...
})
.AddAbpOpenIdConnect("oidc", options =>
{
...
options.Scope.Add("IdentityService");
options.Scope.Add("AdministrationService");
options.Scope.Add("SaasService");
options.Scope.Add("ProductService");
});
There is also related configuration about the Authority, ClientId, ClientSecret under appsettings.json:
"AuthServer": {
"Authority": "https://localhost:44322",
"RequireHttpsMetadata": "true",
"ClientId": "MyProjectName_Web",
"ClientSecret": "1q2w3e*"
},
Blazor.Server
This is the Blazor Server application that is built on top of AspNet Core SignalR with Prometheus configuration on application initialization
app.UseHttpMetrics();
...
app.UseConfiguredEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapMetrics();
});
AuthServer Interaction
This application uses hybrid flow. This client is being seeded in IdentityServerDataSeeder with MyProjectName_BlazorServer client name with all the available scopes.
Since it shares the same flow with Razor/MVC application; same configurations applies to this application type as well.
Angular
This is the SPA application used for back-office application.
Remote Service Call
In the environment.ts file, you can find the configuration for default remote service call and ProductService. They are both set to Web Gateway.
apis: {
default: {
url: 'https://localhost:44325',
rootNamespace: 'MyCompanyName.MyProjectName',
},
ProductService: {
url: 'https://localhost:44325',
rootNamespace: 'MyCompanyName.MyProjectName.ProductService',
},
},
AuthServer Interaction
This application uses authorization_code with PKCE (update). This client is being seeded in IdentityServerDataSeeder with MyProjectName_Angular client name with all the available scopes.
In the environment.ts file, authorization is configured as below to be able to make request to all the api resources and some basic identity resources:
oAuthConfig: {
issuer: 'https://localhost:44322',
redirectUri: baseUrl,
clientId: 'MyProjectName_Angular',
responseType: 'code',
scope:
'offline_access openid profile email phone IdentityService AdministrationService SaasService ProductService',
},
Blazor (Web Assembly)
This is the web assembly application of blazor ui.
AuthServer Interaction
This application uses authorization_code with PKCE (update). This client is being seeded in IdentityServerDataSeeder with MyProjectName_Blazor client name with all the available scopes.
In the BlazorModule authorization is configured as below to be able to make request to all the api resources and some basic identity resources:
private static void ConfigureAuthentication(WebAssemblyHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.Services.AddOidcAuthentication(options =>
{
...
options.ProviderOptions.DefaultScopes.Add("IdentityService");
options.ProviderOptions.DefaultScopes.Add("AdministrationService");
options.ProviderOptions.DefaultScopes.Add("SaasService");
options.ProviderOptions.DefaultScopes.Add("ProductService");
});
}
There is also related configuration about the Authority, ClientId, ResponseType under wwwroot/appsettings.json:
"AuthServer": {
"Authority": "https://localhost:44322",
"ClientId": "MyProjectName_Blazor",
"ResponseType": "code"
},
Public Application (Landing Page)
This is the landing page application of your microservice solution. This application is Razor/MVC simply because of SEO reasons and has no other varieties by default. However it is possible to replace or create a new public application.
This application uses the account related functionality by hosting the Account Module Api but forwarding all the requests to PublicWeb Gateway. So that application can use the functionality of just the Account Module without depending on to whole IdentityService microservice. For more information, do check Module Architecture Best Practices & Conventions Section E.
To achieve this functionality, Public Application needs to reference to Account Module .HttpApi and HttpApi.Client layers to host the api but proxy the request to a remote service.
Remote Service Calls - PublicWeb Gateway
The public application's interactions with the microservices will be through the PublicWeb Gateway. There is a related configuration for remote services in the appsettings.json:
"RemoteServices": {
"Default": {
"BaseUrl": "https://localhost:44353/"
}
},
This configuration indicates the default base url of all the Http Api requests; which is the url of the PublicWeb Gateway for the public application.
AuthServer Interaction
Public application uses hybrid flow and it is being seeded in IdentityServerDataSeeder with MyProjectName_PublicWeb client name with all the available scopes.
In the PublicWebModule authorization is configured as below to be able to make request to AdministrationService and ProductService api resources and some basic identity resources since only these two scopes were allowed in IdentityServerDataSeeder
context.Services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
...
})
.AddCookie("Cookies", options =>
{
...
})
.AddAbpOpenIdConnect("oidc", options =>
{
...
options.Scope.Add("AdministrationService");
options.Scope.Add("ProductService");
});
There is also related configuration about the Authority, ClientId, ClientSecret under appsettings.json:
"AuthServer": {
"Authority": "https://localhost:44322",
"RequireHttpsMetadata": "true",
"ClientId": "MyProjectName_PublicWeb",
"ClientSecret": "1q2w3e*"
},
Updating Scopes
If a new Api Resource and Scope is added to microservice stack;
- Add the new scope to allowed scopes in IdentityServerDataSeeder web/public-web client creation.
- Add the new scope to authentication configuration of the web/public-web application.
UI Development
It is possible to develop UI for the applications with two different ways:
Modular UI Development
Develop the application UI like any abp application template; add UI pages under microservice's .Web project. This way, back-office application will be showing the UI without hosting the microservice application just by using as a remote service. For more information, do check Module Architecture Best Practices & Conventions Section C.
Add microservice UI to back-office application (Web application):
Add HttpApi.Client and .Web projects as references to Web project and add new dependencies to WebModule. Already provided sample is as below:
typeof(ProductServiceWebModule),
typeof(ProductServiceHttpApiClientModule)
ProductService.Web module is designed this way. Examine ProductService.Web project for sample implementation.
This approach may benefit with having the integrity of backend and frontend in a microservice as a whole since it is possible to develop microservice backend and frontend in the same microservice solution.
Monolith UI Development inside application
Develop the application UI inside the application. Add UI pages under application's .Web project. This will allow using microservice as a remote service. You can check Module Architecture Best Practices & Conventions Section D for more information.
Add microservice UI to public-web application (PublicWeb application):
Add HttpApi.Client reference to PublicWeb project and add new dependency to PublicWebModule as below:
typeof(ProductServiceHttpApiClientModule)
ProductService.PublicWeb module is designed this way. Examine ProductService.PublicWeb project for sample implementation.
This way it is possible to separate the frontend and backend teams and develop each of them in their respected solutions.