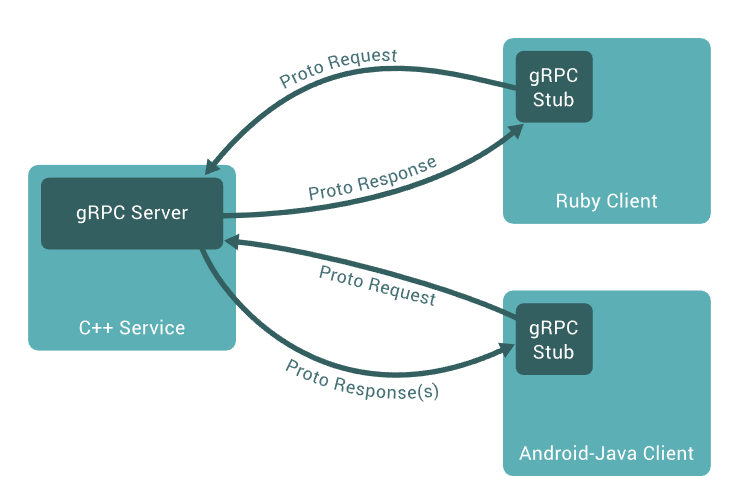
Using gRPC
gRPC is a cross-platform open-source high-performance remote procedure call framework created by Google to be used to provide inter-communication between a large number of microservices. It uses HTTP/2 for the transport layer and Protocol Buffers as the data format to serialize the structured data. It generates cross-platform client and server bindings in different languages with features like authentication, bi-directional streaming and flow control, blocking or non-blocking bindings, cancellation and timeouts.
Benefits
Designed for low latency and high throughput communication, gRPC is great for lightweight microservices where efficiency is critical.
gRPC services can push messages in real-time without polling. Its support for bi-directional streaming makes gRPC an excellent tool for point-to-point real-time communication.
gRPC tooling supports many popular development languages, making gRPC a good choice for multi-language environments.
Protubuf is a lightweight message format. A gRPC message is always smaller than an equivalent JSON message. That can be an important factor of choice where the network environment is constrained.
gRPC can be used to communicate between apps on the same machine. For more information, see Inter-process communication with gRPC.
Using gRPC with the ABP Framework
There are two great articles about gRPC integration to the ABP framework by Halil Ibrahim Kalkan:
- Using gRPC with the ABP Framework | ABP Community
- Consuming gRPC Services from Blazor WebAssembly Application Using gRPC-Web | ABP Community
This guide will explain a scenario where the basket microservice consumes the catalog microservice gRPC service to obtain detailed product information.
Adding a gRPC service to a microservice
We will create a new gRPC service called PublicProductGrpcService under the application layer. This service will be the server for the gRPC communication. We'll start adding tooling for the gRPC service by adding the following packages to the application layer:
<PackageReference Include="Google.Protobuf" Version="3.19.3" />
<PackageReference Include="Grpc.Core" Version="2.42.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Grpc.Tools" Version="2.42.0" PrivateAssets="All" />
Now we shall add a new folder called Protos under the application layer to add the proto files and add product.proto file under it:
syntax = "proto3";
option csharp_namespace = "EShopOnAbp.CatalogService.Grpc";
package CatalogApi;
service ProductPublic {
rpc GetById(ProductRequest) returns (ProductResponse);
}
message ProductRequest {
string id = 1;
}
message ProductResponse {
string id = 1;
string code = 2;
string name = 3;
string imageName = 4;
float price = 5;
int32 stockCount = 6;
}
Now we have defined a new gRPC service called ProductPublic that accepts a ProductRequest complex object containing a string id parameter and returns another complex object named ProductResponse with product properties we desire to return.
Note: The sequence of the properties is important since it will be used for serialization and deserialization order.
To generate the proto definition, update the application layer .csproj file:
<ItemGroup>
<Protobuf Include="Protos\product.proto" GrpcServices="Server" Generator="MSBuild:Compile" />
<Content Include="@(Protobuf)" />
<None Remove="@(Protobuf)" />
</ItemGroup>
This configuration will allow gRPC tooling to generate the gRPC services based on the supplied proto file on compile time. Compile your application layer to generate the gRPC service base class.
Now we can create the application service extending the base class:
public class PublicProductGrpService : ProductPublic.ProductPublicBase
{
private readonly IRepository<Product, Guid> _productRepository;
private readonly IObjectMapper _objectMapper;
public PublicProductGrpService(IRepository<Product, Guid> productRepository, IObjectMapper objectMapper)
{
_productRepository = productRepository;
_objectMapper = objectMapper;
}
public override async Task<ProductResponse> GetById(ProductRequest request, ServerCallContext context)
{
var product = await _productRepository.GetAsync(Guid.Parse(request.Id));
return _objectMapper.Map<Product, ProductResponse>(product);
}
}
This application service containing a single gRPC service method simply gets the product with the provided ID using the product repository and returns the mapped result. You can either use manual mapping or add to the Automapper profile as below:
public class CatalogServiceApplicationAutoMapperProfile : Profile
{
public CatalogServiceApplicationAutoMapperProfile()
{
CreateMap<Product, ProductResponse>();
}
}
To host the gRPC service, add the Grpc.AspNetCore.Server package to the Http.Api.Host layer of your application:
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Grpc.AspNetCore.Server" Version="2.42.0" />
</ItemGroup>
Now we can configure it in the Http.Api.Host module file ConfigureServices method:
context.Services.AddGrpc(options =>
{
options.EnableDetailedErrors = true; // Send detailed error to clients
});
The gRPC server must be hosted using HTTP2 protocol within a different port alongside the default HTTP endpoints. Configure the Kestrel to expose the gRPC using a different end-point by adding a Kestrel section to the appsettings.json in your Http.Api.Host project:
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"Http": {
"Url": "http://localhost:5000",
"Protocols": "Http1AndHttp2"
},
"Https": {
"Url": "https://localhost:44354",
"Protocols": "Http1AndHttp2"
},
"gRPC": {
"Url": "http://localhost:81",
"Protocols": "Http2"
}
}
}
}
This configuration will allow running the gRPC server on port 81 using the HTTP2 protocol and it can be easily overridden on deployment.
The last step for the server side is to configure the ABP endpoints. Update the OnApplicationInitialization method in Http.Api.Host module:
app.UseConfiguredEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapGrpcService<PublicProductGrpService>();
});
This configuration will map incoming gRPC requests to the gRPC service we have defined.
Consuming the added gRPC service from another microservice
We will be using the Basket microservice to consume the PublicProductGrpService we have created at the catalog microservice.
Start with adding the tooling to the Basket microservice application layer:
<PackageReference Include="Google.Protobuf" Version="3.19.3" />
<PackageReference Include="Grpc.Net.ClientFactory" Version="2.42.0" />
<PackageReference Include="Grpc.Tools" Version="2.42.0" PrivateAssets="All" />
We also need to configure the basket microservice as gRPC client service to consume the proto:
<ItemGroup>
<Protobuf Include="..\..\..\catalog\src\EShopOnAbp.CatalogService.Application\Protos\product.proto" GrpcServices="Client" />
</ItemGroup>
This configuration allows us to use the same proto generated by the Catalog microservice.
Since the Basket microservice will be using HTTP and gRPC to communicate with the Catalog microservice, we need to configure the remote service endpoints of the Basket microservice and provide which endpoint of remote service will be used for HTTP and which for gRPC. Add a RemoteServices section to appsettings.json of your BasketService host layer:
"RemoteServices": {
"Catalog": {
"BaseUrl": "https://localhost:44354/",
"GrpcUrl": "http://localhost:81"
}
},
Note: The gRPC endpoint URL must match with the gRPC server endpoint, which is configured at Catalog microservice Kestrel configuration.
Now we can add a gRPC client in the ConfigureServices method of the Basket microservice host application module:
context.Services.AddGrpcClient<ProductPublic.ProductPublicClient>((services, options) =>
{
var remoteServiceOptions = services.GetRequiredService<IOptionsMonitor<AbpRemoteServiceOptions>>().CurrentValue;
var catalogServiceConfiguration = remoteServiceOptions.RemoteServices.GetConfigurationOrDefault("Catalog");
var catalogGrpcUrl = catalogServiceConfiguration.GetOrDefault("GrpcUrl");
options.Address = new Uri(catalogGrpcUrl);
});
This configuration will extract the gRPCUrl which is provided in the appsettings RemoteServices section.
Now you can use the gRPC service client in any application service by simply injecting it:
public class BasketProductService : IBasketProductService, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly ILogger<BasketProductService> _logger;
private readonly ProductPublic.ProductPublicClient _productPublicGrpcClient;
public BasketProductService(
ILogger<BasketProductService> logger,
ProductPublic.ProductPublicClient productPublicGrpcClient)
{
_logger = logger;
_productPublicGrpcClient = productPublicGrpcClient;
}
private async Task<ProductDto> GetAsync(Guid productId)
{
var request = new ProductRequest { Id = productId.ToString() };
_logger.LogInformation("=== GRPC request {@request}", request);
var response = await _productPublicGrpcClient.GetByIdAsync(request);
_logger.LogInformation("=== GRPC response {@response}", response);
return _mapper.Map<ProductResponse, ProductDto>(response) ??
throw new UserFriendlyException(BasketServiceDomainErrorCodes.ProductNotFound);
}
}
Using Code-first gRPC services and clients
Instead of manually creating the proto files, you can also use protobuff-net.Grpc library to create your services and contracts.
See Code-first gRPC services and clients with .NET for more details.
You can use your back-office or your public-web application to call gRPC services. There is a great community post about Consuming gRPC Services from Blazor WebAssembly Application Using gRPC-Web with detail explanation and source-code.
Authorization on gRPC Services
You may have defined permissions for your gRPC services. When initiating a gRPC call, add the Authorization header with Bearer {access_token}. If you are using protobuff-net.Grpc, you can set it as below:
var accessTokenResult = // Get access_token from TokenProvider (BlazorWasm) or IHttpAccessor (Mvc)
var credentials = CallCredentials.FromInterceptor(async (context, metadata) =>
{
metadata.Add("Authorization", $"Bearer {accessToken}");
});
credentials = CallCredentials.FromInterceptor(async (context, metadata) =>
{
metadata.Add("Authorization", $"Bearer {accessToken}");
});
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:10042", new GrpcChannelOptions
{
HttpHandler = new GrpcWebHandler(new HttpClientHandler()),
Credentials = ChannelCredentials.Create(new SslCredentials(), credentials)
});
var productAppService = channel.CreateGrpcService<IProductAppService>();
Products = await productAppService.GetListAsync();
The metadata will be the headers sent with the gRPC requests. When the request is made, you may come across with an error:
The response was successfully returned as a challenge-response: {
"error": "invalid_token",
"error_description": "The issuer associated with the specified token is not valid.",
"error_uri": "https://documentation.openiddict.com/errors/ID2088"
}
This is because the token is being obtained from the browser, which is a different issuer. Since the application has two different URLs, one for the browser and one for the gRPC, the OpenID-provider will not validate the issuer. To solve the problem, add the URL of the gRPC channel to the toke validation parameters valid issuers list.
Navigate to your AuthServer project and under the PreConfigureServices method:
PreConfigure<OpenIddictBuilder>(builder =>
{
builder.AddValidation(options =>
{
options.AddAudiences("ProductManagement");
options.UseLocalServer();
options.UseAspNetCore();
options.Configure(validationOptions => validationOptions.TokenValidationParameters.ValidIssuers = new[]
{
"https://localhost:44388", //AuthServer Url
"https://localhost:44388/",
"https://localhost:10042", //gRPC channel
"https://localhost:10042/"
});
});
});
MultiTenancy on gRPC Services
When the multi-tenancy is active in your project, you need to send the tenant information with the header on the request. This is done automatically with the default ABP HTTP requests. Since the gRPC requests are initiated through a different channel, the tenant information must be added manually to the header, like the Authorization header.
var grpcChannelOptions = new GrpcChannelOptions
{
HttpHandler = new GrpcWebHandler(new HttpClientHandler())
};
if (CurrentTenant.IsAvailable) // No need to add header if it's Host
{
var credentials = CallCredentials.FromInterceptor(async (context, metadata) =>
{
metadata.Add("__tenant", CurrentTenant.Name);
});
grpcChannelOptions.Credentials = ChannelCredentials.Create(new SslCredentials(), credentials);
}
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:10042", grpcChannelOptions);
var productAppService = channel.CreateGrpcService<IProductAppService>();
Products = await productAppService.GetListAsync();
Sample
You can examine the eShopOnAbp.BasketService and the eShopOnAbp.CatalogService.
You can examine the GrpcDemo2 and the Blazor web app.